Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: This post focuses on the in-place upgrade on Windows, exploring what it does, when it's used, its benefits, limitations, and what makes it different from a clean install. -From m3datarecovery.com

For general Windows users, running the Windows Update from the Settings app is the most straightforward way to perform a system update. This post focuses on the in-place upgrade, which many users may not be familiar with.
What does an in-place upgrade do? What can we benefit from it? What should we pay attention to about performing an in-place upgrade? This post covers everything about the Windows in-place upgrade we may be concerned with.
Note: In-place upgrade on Windows is just to upgrade your current system, with all content remaining. If you need to perform a clean install, you should download the Windows ISO and create a bootable USB installer. Follow:
Download Windows 11 ISO
Download Windows 10 ISO
Download Windows 10 Home ISO
Download Windows 10 Pro ISO
What does an in-place upgrade do on Windows
An in-place upgrade on Windows refers to the process of upgrading your current Windows system to a newer version (e.g., from Windows 10 to Windows 11) while preserving personal files, installed applications, and modified settings.
With an in-place upgrade, for example, we can upgrade from Windows 10 to Windows 11 without losing existing files, apps, and settings, which is a far cry from what a Clean Install does.
In-place upgrade saves us the trouble of restoring data from the backup copy, reinstalling third-party apps, and resetting preferred settings, so it's often considered the most effort-saving way for upgrading to a newer Windows version. 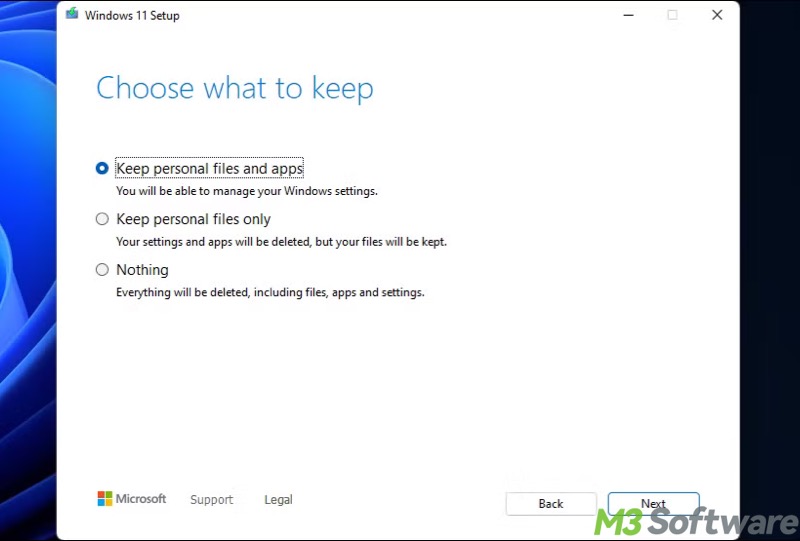
You can tap on the buttons below to share the post
When an in-place upgrade is used on Windows
An in-place upgrade on Windows is often used when:
- When we tend to upgrade the system to a newer version without losing data and apps.
- When we don't want to waste much time and effort on a Clean Install.
- When we encounter a system update failure and error.
- When we run into system file corruption that SFC (System File Checker) cannot repair.
Limitations or downsides of an in-place upgrade
With respect to the in-place upgrade on Windows, here are some risks we should pay attention to:
- Carried-over system issues: If the system issues, like corruption, are deeply-rooted, an in-place upgrade may fail to fix them.
- Disk space requirement: An in-place upgrade typically needs several GBs of free disk space.
- Potential data loss: Unexpected problems or interruptions may cause data loss.
- Auto rollback: If an in-place upgrade fails, Windows usually rolls back to the previous version automatically.
Note: Though an in-place upgrade preserves your data, it's always advisable to back up data on Windows before performing it.
Difference between in-place upgrade and clean install
The comparison table below concisely explains how an in-place upgrade is different from a clean install:
| Features | In-Place Upgrade | Clean Install |
| Keeps personal files | Yes | No |
| Keeps installed apps | Yes | No |
| Keeps settings | Yes | No |
| Installation media | Required | Not required |
| Fresh system files | Yes | Yes |
| How long it takes | 30-90 minutes | Longer |
Tips: We should choose a clean install over an in-place upgrade when the system is severely corrupted, infected, or the system issue recurs constantly after an in-place upgrade.
Conclusion
A Windows in-place upgrade is essentially a system upgrade (e.g., from Windows 10 to Windows 11) that keeps personal files, installed applications, and settings intact. It's often used when users want to upgrade Windows to a newer version without losing data, especially when system update errors appear. However, it's always recommended to back up important data before doing it.
Please share this post if you find it helpful
FAQs about in-place upgrade
An in-place upgrade refers to the process of reinstalling or upgrading Windows while keeping personal files, installed apps, and most settings intact. This is the biggest advantage of an in-place upgrade, particularly when compared with a clean install on Windows.
Windows users often choose an in-place upgrade to: 1. Upgrade Windows to a newer version (e.g., from Windows 10 to Windows 11). 2. Repair system update failure and error. 3. Fix system file corruption that SFC (System File Checker) cannot repair. 4. Apply a feature update when Windows Update isn’t working.
Matters needing attention before an in-place upgrade: 1. Enough free disk space (20-30GBs). 2. Back up important data. 3. A Windows installation media. 4. Stable power supply. 5. Ensure the system is not heavily corrupted or infected.
