Written by
Yuri ZhangAccidentally deleting a Windows system file is like pulling a Jenga block from the bottom of a tower. One wrong click, one hasty cleanup, and suddenly your computer is glitching, freezing, or failing to boot at all.
Time is critical. The longer you wait, the higher the chance that newly created files will overwrite the deleted ones, making recovery far more difficult. Now let's delve into how to remedy accidentally deleting Windows system files instantly.
If our PC still boots after accidentally deleting system files
If our system is still running normally, follow these steps to repair the damage safely. Before anything else, check if the deleted system files are in the Recycle Bin. If so, restore them.
Method 1. Run System File Checker (SFC)
SFC is a built-in Windows tool that scans for missing or corrupted system files and replaces them with original copies. Here are steps to run it:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator by searching for it in the Start Menu and right-clicking on it.
- Type:sfc /scannow
- Press Enter and let it scan. It may take several minutes.
If SFC finds issues, it will attempt to repair them automatically.
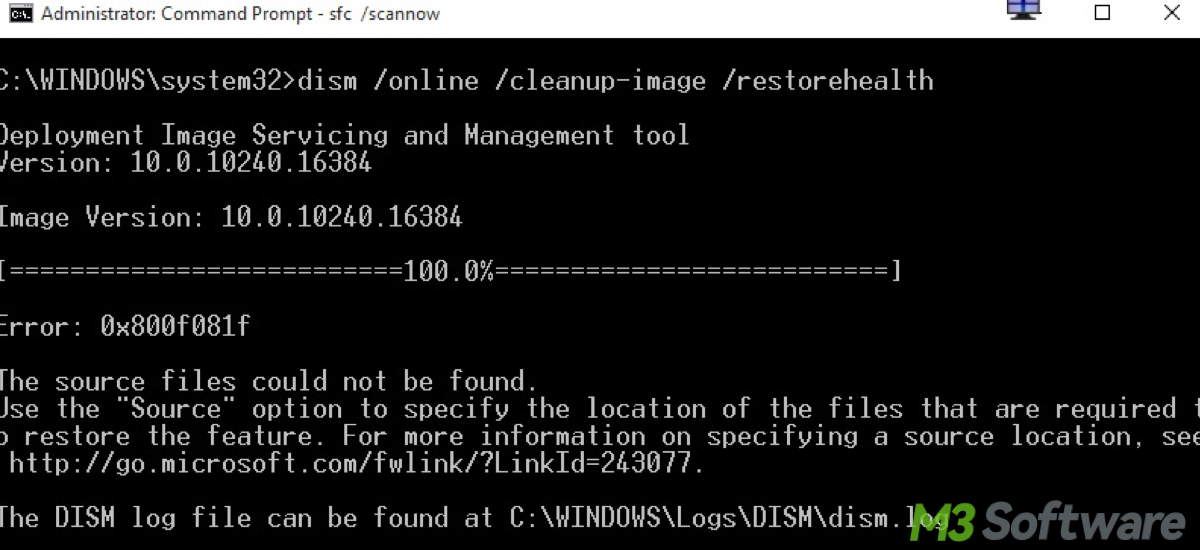
Method 2. Use DISM for deep-level repair
If SFC can't fix everything, use DISM (Deployment Imaging Servicing and Management) by running the command:DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
This fetches clean files from Windows Update and repairs the system image.
Share this if you find it worked.
If our PC can't boot after accidentally deleting system files
When our system refuses to start after deleting system files, here's what to do:
Method 1: Run SFC on an offline system
- To boot into Windows Recovery Environment: Interrupting boot 3 times to trigger recovery mode, or booting from a Windows installation USB.
- Once in the Advanced Options, choose Command Prompt.
- Use this command to scan an offline Windows installation:sfc /scannow /offbootdir=C:\ /offwindir=C:\Windows
If you're not sure about the drive letters, use the diskpart → list volume command to find where Windows is located (it might be D: in recovery mode).
Method 2. Use System Restore
If you previously created a restore point, go to Advanced Options as above > System Restore. Then choose a point before the deletion and let Windows restore your system files
Warning: If none of the above work, you can reset or reinstall Windows as a last resort: First, boot from a Windows installation USB, then choose Repair your computer > Reset this PC. Lastly, opt to keep your files (if desired), but this will remove apps.
How to prevent this in the future:
- Avoid modifying or deleting anything in C:\Windows.
- Enable System Restore.
- Keep a system backup using iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Windows via system clone.
- Use File History or OneDrive to protect personal files.
What are Windows system files?
System files are critical components that allow your Windows operating system to function properly. These include:
- .dll (Dynamic Link Library) files
- .exe system executables
- .sys system drivers
- Boot-related files like bootmgr, winload.exe, etc.
Deleting these can cause error messages, missing features, or prevent your computer from starting at all.
Final thought
Note that you may want to use data recovery software to restore specific files, however, recovered system files may not restore full functionality. The system might still behave abnormally or fail to boot. Here's why.
Simply recovering the file doesn't always fix the problem, especially if it's a protected Windows file, or its dependencies are broken, or permissions are affected. For crucial system files, System Restore or System File Checker is more suitable.
Deleting system files can be scary, the key is to act quickly, avoid overwriting files, and let built-in recovery tools do the heavy lifting. If your system still isn't back to normal, consider seeking professional help or reinstalling Windows. And remember to back up vital data this time, which can be achieved through iBoysoft DiskGeeker.
Share this if you have learned every option to restore your digital lifeline.
