Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: This article is structured around primary vs extended vs logical partition on Windows. The role they play, the key differences, and the links between them are elaborated. -From m3datarecovery.com
In Windows, disk partitions are used to organize and manage the storage on a hard drive or solid-state drive (SSD). From a macro perspective, there are 3 major types of disk partitions on Windows: primary partition, extended partition, and logical partition.
This article focuses on the primary vs extended vs logical partition on a Windows computer. You will clearly understand the differences and connections between them.
Note: Given the fact that GUID Partition Table (GPT) does not use extended or logical partitions, primary vs extended vs logical partition are primarily discussed in the context of the MBR (Master Boot Record) partition scheme.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Primary partition
This chapter introduces what the primary partition is and its primary role in the MBR (Master Boot Record) partition scheme on Windows.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - What is the primary partition
A primary partition is the main type of disk partition that can directly store a bootable operating system (e.g., Windows OS) or other general data.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Primary role of primary partition
The boot files (e.g., bootmgr, Boot Configuration Data, bootloaders) required to start up your Windows PC can only be saved on a primary partition, which, at the same time, must be marked as "active". This active partition is commonly labeled the “System Partition”, “System Reserved Partition”, or “EFI System Partition” on Windows.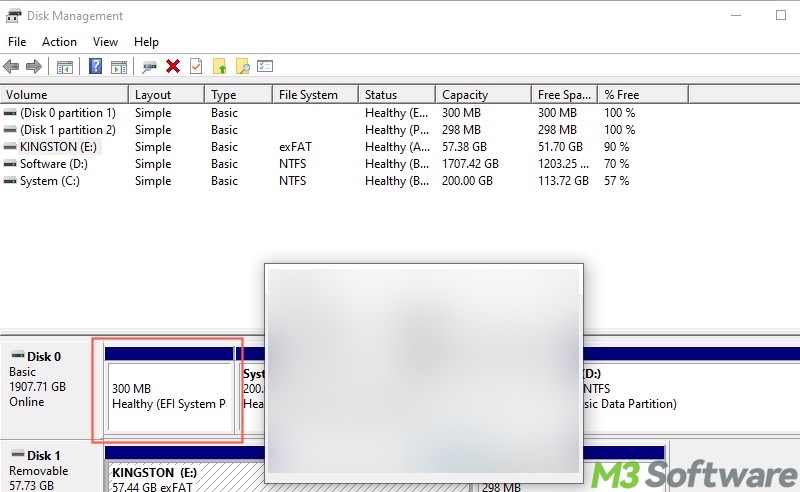
The primary partition, generally the separate one, can also be used to store the Windows operating system files (e.g, Windows folder, Program Files, Users folder). In other words, it is a partition where Windows is installed, and it is commonly labeled the “Boot” or “C:” partition on Windows.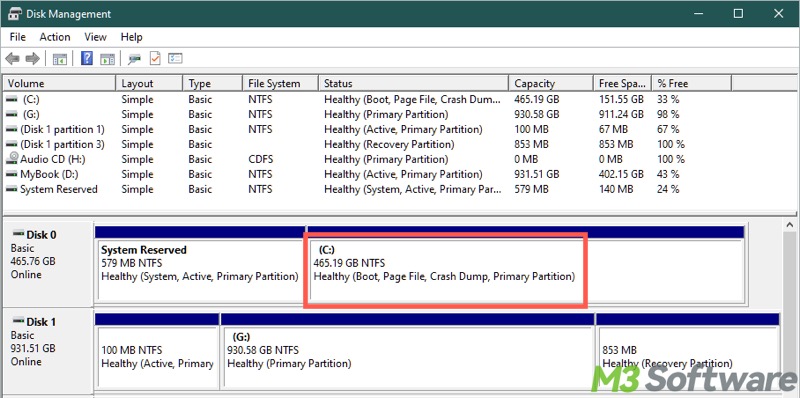
Of course, you can choose a primary partition for general data storage, as long as the primary partition is formatted with a supported file system and there's free space on it.
Pay attention to the difference between system partition and boot partition on Windows.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Limits of primary partition
- Primary partitions only exist in the MBR (Master Boot Record) partition scheme
- On an MBR-formatted disk, you can have up to 4 primary partitions or 3 primary partitions + 1 extended partition.
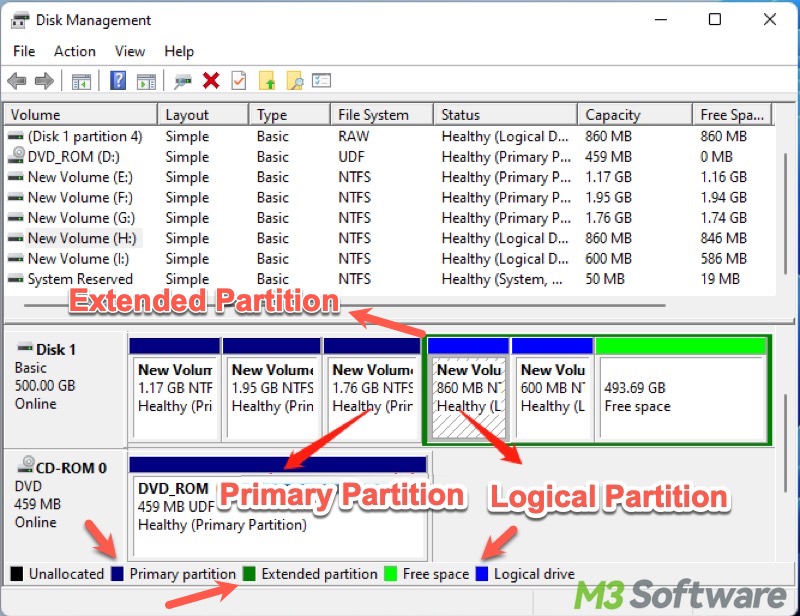
- There must be one primary partition marked as "active" to store the boot files required to start your Windows PC.
- There can be only one active partition per physical hard disk.
- Up to 2 TB per partition.
The buttons below help share the article quickly
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Extended partition
This part explores extended partition and its primary role in the MBR (Master Boot Record) partition scheme on Windows.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - What is the extended partition
Let's look back on what we discussed before: On an MBR-formatted hard disk, you can have up to 4 primary partitions or 3 primary partitions + 1 extended partition. If you need more than 4 partitions on a hard disk, an extended partition will help.
An extended partition is a special type of partition that enables you to break through the limit of having only 4 partitions on a hard disk formatted with the MBR partition scheme.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Primary role of extended partition
An extended partition serves as a container for logical partitions. On an MBR-formatted disk, you can have only one extended partition, but you are allowed to create up to 128 logical partitions for data storage and management.
The extended partition plays a critical role in dividing the free space on the hard disk for numerous logical partitions.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Limits of extended partition
- The extended partition only exists in the MBR (Master Boot Record) partition scheme.
- You can only have one extended partition on a disk.
- An extended partition cannot be set active or bootable, which means it cannot be used to store boot files.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Logical partition
This chapter guides you through logical partition, its role, and limits in the MBR (Master Boot Record) partition scheme on Windows.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - What is the logical partition
A logical partition is a type of partition that exists only within an extended partition. Theoretically, you are allowed to create up to 128 logical partitions inside an extended partition on an MBR-formatted disk.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Primary role of extended partition
A logical partition inside an extended partition acts like a normal drive where you can store any files you want, including software, applications, programs, etc.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Limits of logical partition
- Logical partitions exist only inside an extended partition.
- Logical partitions are not directly created inside the extended partition, meaning that you need to manually create one or more logical partitions.
- Logical partitions are usually not bootable, though it's technically possible to set up a bootable one.
- The number of logical partitions is theoretically unlimited and is only limited by the size of the extended partition.
Primary vs extended vs logical partition - Summary
| Attribute | Primary Partition | Extended Partition | Logical Partition |
| Location | Directly on the disk | Directly on the disk | Only exists inside extended partition |
| Purpose | Store boot files, system files, or general data | Divide free disk space by creating logical partitions | Store general data or bootable OS (advanced configurations needed) |
| Number Allowed in MBR | Up to 4 | Only 1 | Theoretically unlimited |
| Bootable | Yes! The active partition must be a primary partition. | No! | Technically possible! |
| Must be created in MBR? | Yes! | No! | No! |
FAQs about primary vs extended vs logical partition
You can share this post by tapping on the following buttons
On an MBR-formatted disk, you can have up to 4 primary partitions or 3 primary partitions + 1 extended partition. Compared to the GPT (GUID Partition Table) partitioning scheme, the MBR (Master Boot Record) was introduced in the early 1980s, when disk space was low and precious. If you want to divide your hard disks by having more partitions, you can create logical partitions inside an extended partition.
The answer depends on what data you are saving. In Windows, it is undoubtedly correct to choose primary partitions for keeping boot files or system files. For general data, primary partitions and logical partitions are both ideal choices. In comparison with primary partitions, logical partitions help you further segment a hard disk for various purposes.
Primary partitions are used for boot files, Windows OS files, or general data, and are limited in number (up to 4 in MBR). Logical partitions are created inside an extended partition and are usually used for data storage. An extended partition (only 1 in MBR) serves as a container for logical partitions.
