Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: The Task Manager on Windows is a powerful utility that enables you to manage processes and monitor hardware performance in real-time. This article focuses on what Task Manager does and how to open it on Windows. -From m3datarecovery.com
In a nutshell, the Task Manager on Windows is a built-in utility that enables Windows users to monitor and manage what a Windows computer is doing in real-time.
The Task Manager on Windows provides important information, including the processes, apps, or services currently running, as well as hardware resource usage. More importantly, if something goes wrong, you can end, stop, or restart the process to fix the issue. Check out the following content for more details.
What you can do with the Task Manager on Windows 10/11
This chapter introduces the actions you can take in the Task Manager on Windows, which offers great convenience for viewing and controlling what's happening on your Windows computer.
You can share the post by tapping on the buttons below
Monitor and manage running processes via the Task Manager on Windows 10/11
With the Processes tab in the Task Manager on Windows, you can view and monitor all processes, programs, and applications that are currently active. When you right-click on each of the processes under the "Processes" tab, you are provided with several practical options in the right-click menu.
For example, the "End task" option can be particularly helpful when a process, application, or program becomes unresponsive or causes glitches. It serves as a way to terminate the processes forcibly. 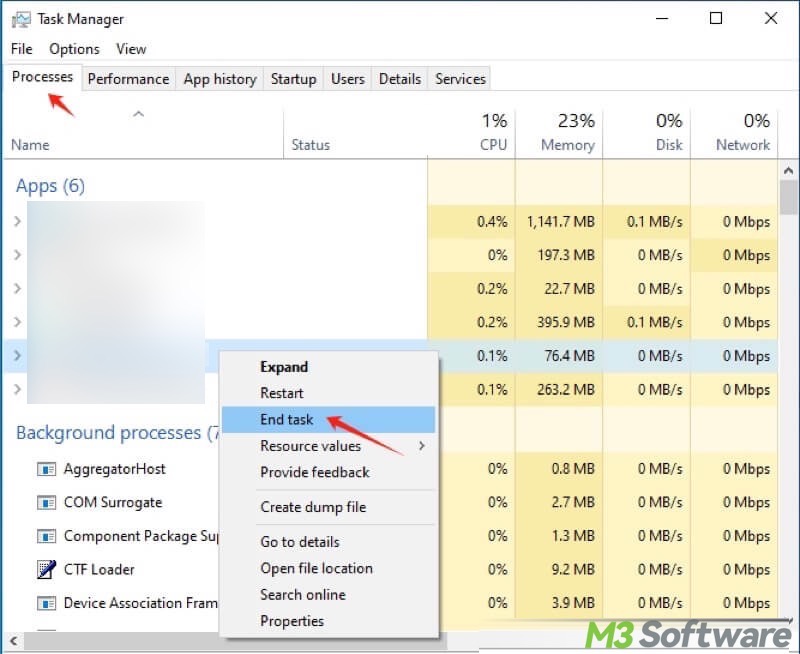
The "Details" tab offers a more technical list of every process with details like Process ID (PID), status, and memory usage. 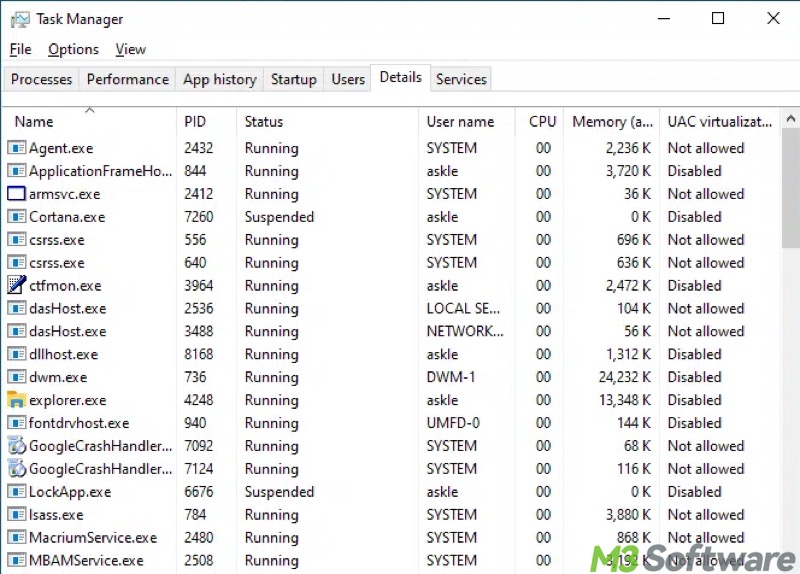
Monitor hardware performance and usage via the Task Manager on Windows 10/11
Besides how much of your computer's resources each process, application, or program is using, the Task Manager on Windows provides graphs and stats for CPU, GPU, RAM (memory), disk, and network activity and usage.
The detailed graphs and stats are displayed under the "Performance" in the Task Manager on Windows. For example, here's what the memory performance looks like in the Windows 10 Task Manager: 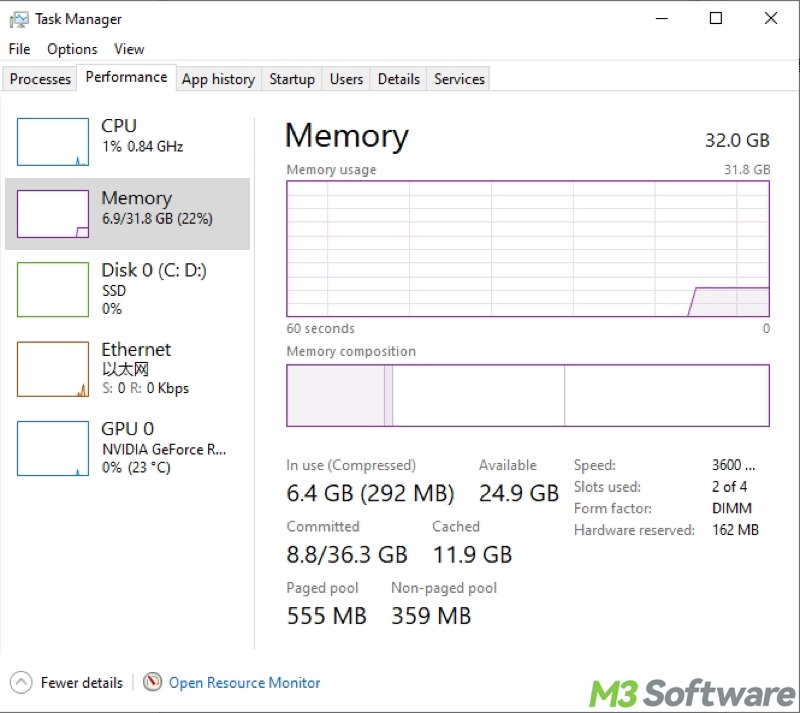
Control startup items via the Task Manager on Windows 10/11
The "Startup" tab in the Task Manager on Windows allows you to control which apps or programs automatically run during the Windows startup. Excessive startup items can cause a slow Windows 10 startup.
Therefore, you can disable the startup item by right-clicking on it. 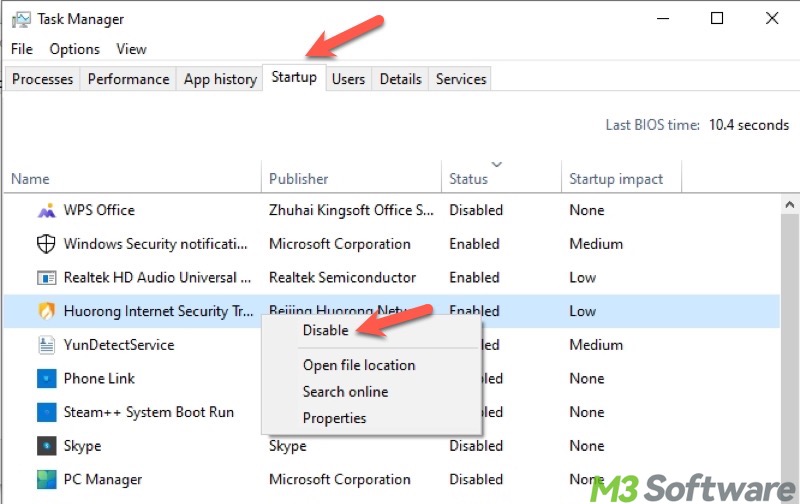
Manage logged-in users via the Task Manager on Windows 10/11
With the "Users" tab in the Task Manager on Windows, you can view all the logged-in users and check which is consuming the most resources on shared systems. By right-clicking on the users under this tab, you can connect/disconnect, sign off, or switch user accounts. 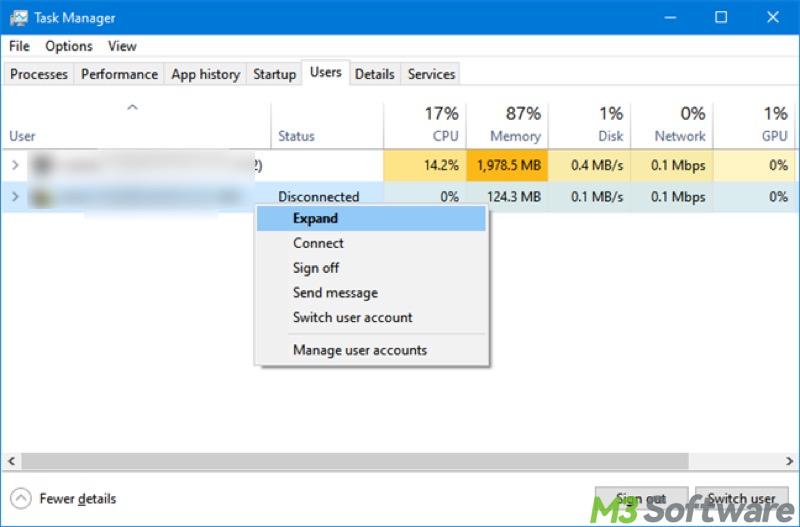
Manage background services via the Task Manager on Windows 10/11
The "Services" tab in the Task Manager on Windows shows all the Windows services running in the background and their current status. Under this tab, you can quickly start, stop, or restart services. 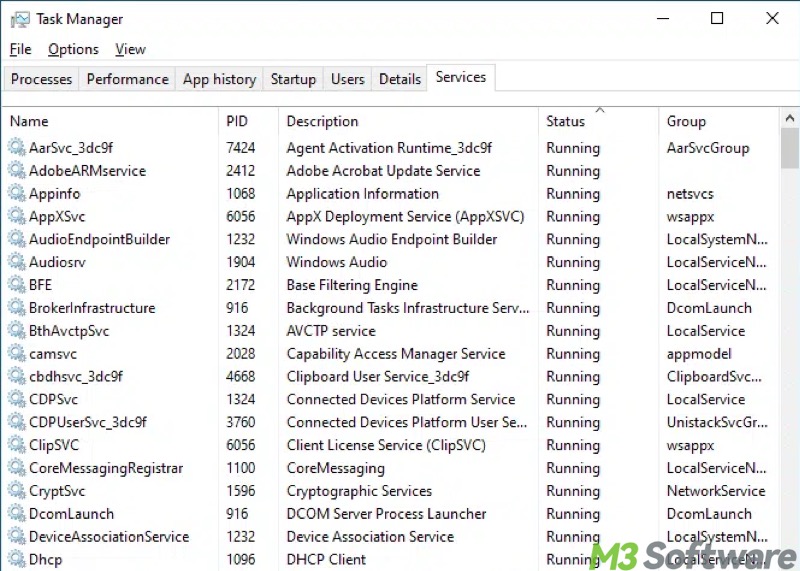
How to open Task Manager on Windows 10/11
There are various methods to open the Task Manager on Windows 10/11, so you can choose one based on your needs.
Open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the Start menu
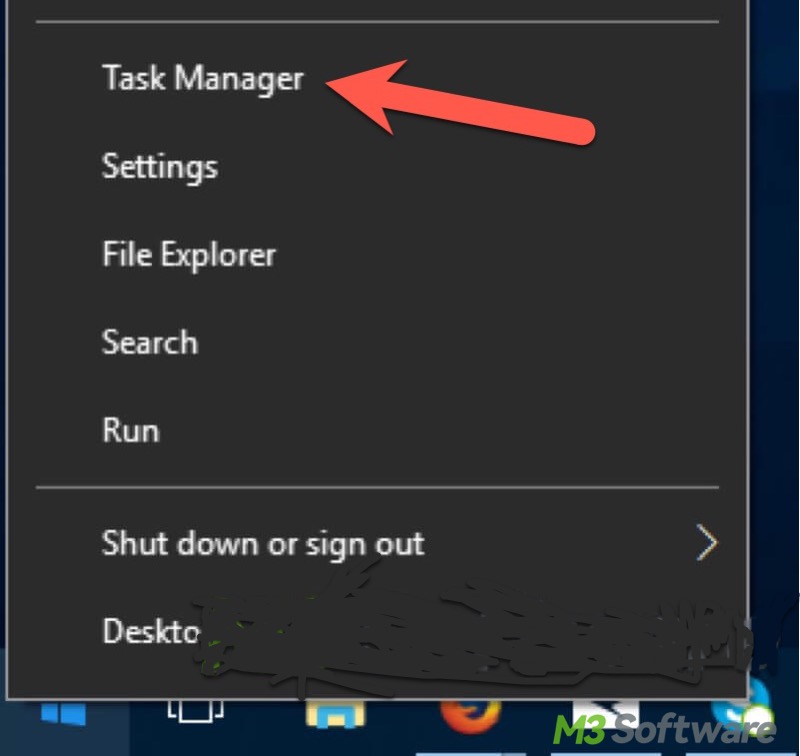
Here's how to open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the Start menu:
- Right-click on the "Start" menu button on Windows.
- Choose "Task Manager" from the list.
Open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the taskbar
Here's how to open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the taskbar:
- Right-click on the taskbar on Windows, and then choose "Task Manager" from the menu.
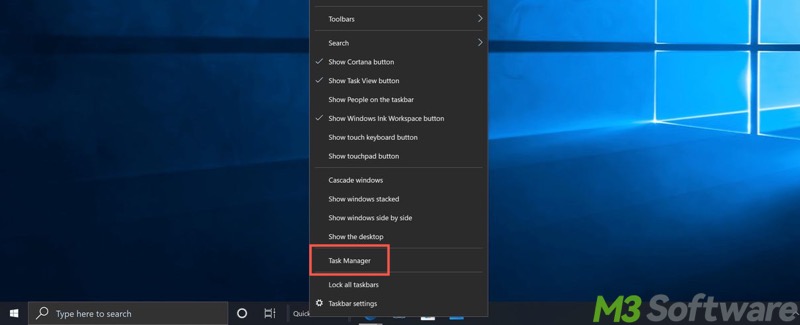
- Alternatively, press the "Windows+X" keys to select "Task Manager."
Open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the shortcut
The Windows Task Manager shortcut: Ctrl+Shift+Esc keys on your keyboard
Open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the Windows search box
Here's how to open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the Windows search box.
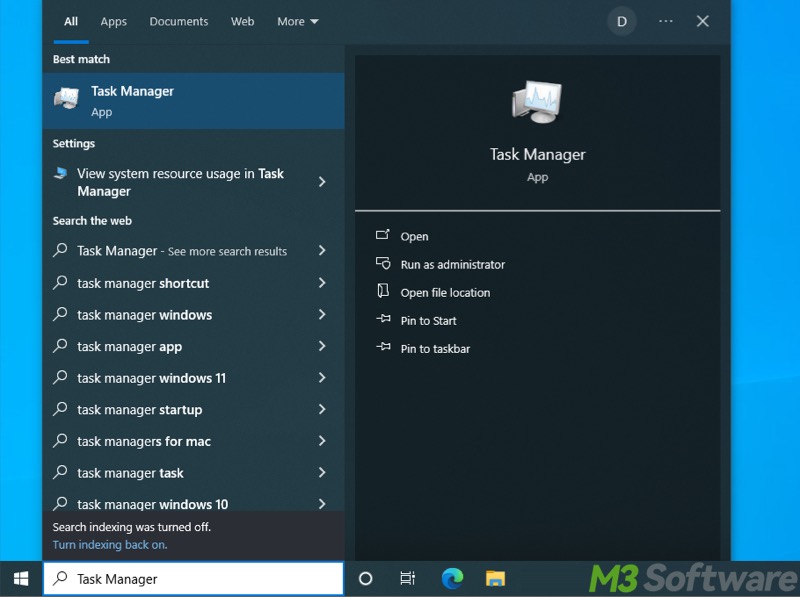
- Press the "Windows+S" keys to launch the Windows search box. Alternatively, tap on the search box in the lower left corner.
- Input "Task Manager" and click the result to open it.
Open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the Run dialog box
The “Run” dialog box is a small window that enables you to quickly open programs without navigating through menus. Here's how to open Task Manager on Windows 10/11 through the “Run” dialog box:
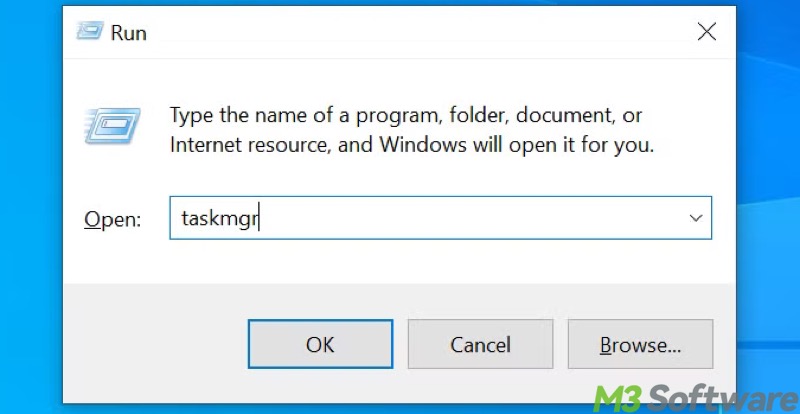
- Press the "Windows+R" keys to launch the "Run" dialog box.
- Input "taskmgr" and click the "OK" button or hit the "Enter" key to open Task Manager.
Also read:
What do you make of this article? You can share it with your friends!
FAQs about Task Manager on Windows
For a typical Windows PC user, the Task Manager can be used to: 1. View and monitor the running processes, programs, applications, and services. 2. Check hardware usage, including CPU, GPU, RAM, hard disk, and network. 3. Force-end unresponsive tasks. 4. Manage startup items. 5. Check user sessions and app history.
Task Manager is a critical built-in utility on Windows that helps users view and manage running processes, programs, applications, and system performance in real-time.
Pressing the Ctrl+Shift+Esc keys on your keyboard is the most common way to open Task Manager. Alternatively, you can open Task Manager by right-clicking on the Start menu button or the Taskbar. The Windows search box is another tool that can help you access the Task Manager.
