Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: This post revolves around USB flash drive vs SSD on Windows, exploring their differences in connection, performance, usage, storage capacity, and other aspects. -From m3datarecovery.com

On a modern Windows PC, an SSD (solid-state drive) has similarities to a USB flash drive, as they both serve as non-volatile storage (flash memory). Nevertheless, SSDs and USB flash drives differ considerably in several respects.
This post focuses on the USB flash drive vs SSD, elaborating on the distinctions in various terms, particularly in terms of performance, usage, and other factors that Windows users are concerned with.
You can click the following buttons to share the article
USB Flash Drive vs SSD
You can refer to the following contents to decide which one to choose based on different situations.
USB Flash Drive vs SSD - Connection
The physical shape and connection can be the most intuitive difference that Windows users can notice.
- USB flash drive: A USB flash drive connects to a Windows computer through a USB interface. It's considered a removable storage device because of its properties like "hot-swap" and "plug-and-play."

- SSD: An SSD typically connects via the SATA or NVMe (PCIe) interfaces. The following form factors are commonly found in modern laptops and desktops.

USB Flash Drive vs SSD - Storage size
Generally speaking, we can't distinguish a USB flash drive from an SSD based on the storage space, but the maximum storage size of an SSD can be higher than that of a USB flash drive.
- USB Flash Drive: The USB flash drives from 4 GB to 1 TB are popular with Windows computer users.
- SSD: SSDs are available in large capacities, from 120 GB to several TB (terabytes).
USB Flash Drive vs SSD - Performance
According to the different standards, interfaces, or technologies they use, there's a big difference in the performance they can deliver.
- USB Flash Drive: The read-write speeds of USB flash drives vary from 30 to 200 MB/s, depending on the standards, such as USB 2.0, 3.0, or 3.2.
- SSD: The read-write speeds can range from 500 MB/s to 5000+ MB/s. NVMe (PCIe 4.0/5.0) SSD > M.2/U.2 NVMe (PCIe 3.0) SSD > SATA SSD
USB Flash Drive vs SSD - Lifespan
- USB Flash Drive: A USB flash drive made with general flash memory can wear out easily if it's frequently used for system use or heavy writes.
- SSD: The premium controllers and NAND make it adaptable to constant, heavy reads/writes. TRIM, Wear leveling, TBW (Terabytes Written), or DWPD (Drive Writes Per Day) ensure a longer lifespan.
USB Flash Drive vs SSD - Usage
Here's what a USB flash drive or an SSD is used for in modern laptops and desktops.
- USB Flash Drive: Given its portability and hot-swap properties, it's considered a removable storage device and primarily used for file transfer, temporary backup, and temporary storage. Obviously, a USB flash drive is unsuitable for running Windows or applications.
- SSD: The TRIM and other advanced features make it perfect for installing and running Windows operating systems, software, applications, and more. Of course, it's an ideal storage medium to house all your personal data.
USB Flash Drive vs SSD - Recognition
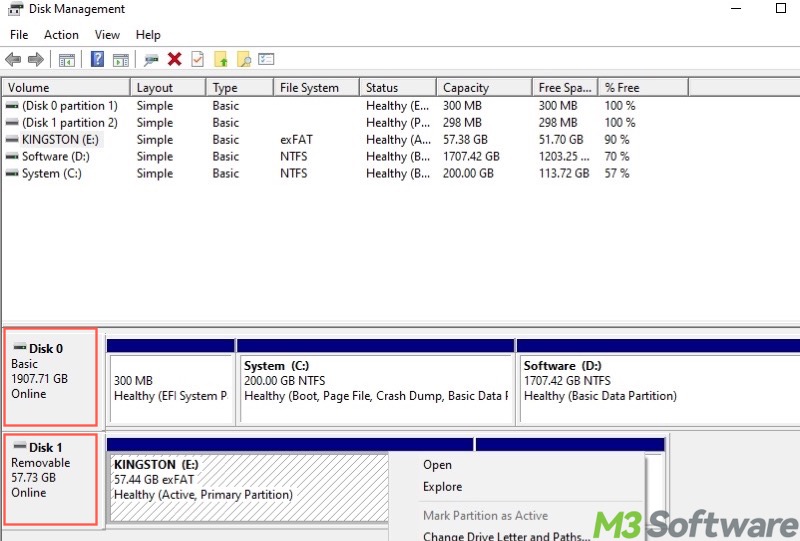
- USB Flash Drive: A USB flash drive shows up in Disk Management as a "Disk" as well, but it's marked as "Removable."
- SSD: An SSD shows up in Disk Management as a "Disk", which is typically marked as "Basic." Windows users often partition an SSD for different purposes.
Also read:
Conclusion
A USB flash drive is ideal for temporary file transfer, storage, or backup because of its portability, storage capacity, and performance. On the contrary, an SSD is perfect for long-term storage and constant, heavy writes, so installing and running Windows on an SSD is recommended.
You can share the post by tapping on the buttons below
FAQs about USB flash drive vs SSD
Though both USB flash drives and SSDs use flash memory, they differ in design, performance, durability, and purposes. A USB flash drive is portable, small, and primarily for temporary file transfer, storage, and backup. An SSD is a primary storage device meant for computers.
SSDs often use NVMe/PCIe interfaces and other advanced technologies, read/write speeds can reach 500 MB/s to 5000+ MB/s. Flash drives usually have slower controllers and USB interfaces (commonly 20–400 MB/s).
Not recommended, as USB flash drives are not designed for heavy, continuous read/write like SSDs. Otherwise, USB flash drives wear out quickly.
