Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: This post revolves around the quick format vs full format in Windows and mainly discusses the key differences between them. Detailed steps to quickly or fully format a drive in Windows are included. -From m3datarecovery.com

Formatting in Windows often comes into play when users want to prepare a new or old storage device for use, as formatting typically aims to set up a file system (such as NTFS, exFAT, or FAT32) and erase all the data on the drive. It also works like a charm in repurposing a drive or repairing corruption.
This post covers everything you need to know about quick format vs. full format. Understanding the key differences between quick and full format is crucial for organizing and managing the files on the drive.
Reddit discussions on quick format vs full format
There are heated discussions on quick format vs full format in the post on Reddit, where computer users explain how the files on the drive are affected when performing quick or full format, and which option is recommended in certain cases.
You can open the following Reddit post and view more details about the discussions on quick format vs full format.
Difference between quick format and slow format?
by u/aaronryder773 in DataHoarder
Quick format vs full format - what do they have in common
Before elaborating on full format vs quick format in Windows OS, it is worth noting that there are some things that both quick format and full format share in common in Windows:
- Both quick and full format delete the file system table, which removes references to the files, but the data remains on the drive until they are overwritten.
- Both quick format and full format set up a new file system, such as NTFS, FAT32, or exFAT.
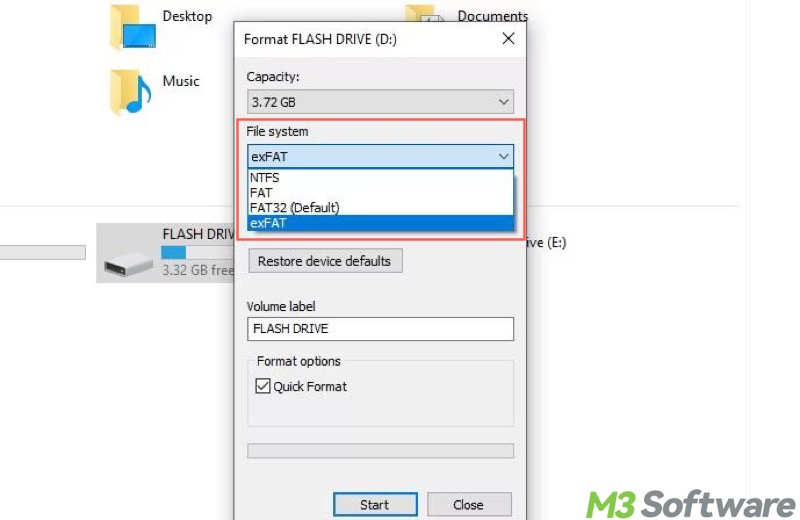
- Both quick format and full format can be performed through File Explorer, Disk Management, or Command Prompt.
You can share this post by clicking the buttons below
Quick format vs full format - how is the data processed
Deleting all the data on the drive is often considered the biggest move in formatting, but the biggest difference between quick format and full format also lies in data deletion.
- Quick Format - Quick Format erases all the data on the drive and marks the disk space as available. It does not perform the overwriting, which means the erased data can be recovered, typically using a specialized data recovery tool, until the new data overwrites it.
- Full Format - Full Format not only erases all the data on the drive but also may overwrite some of the data while checking the bad sectors and writing new file system structures, making it harder for users to recover the erased data, even with a specialized tool.
As a side note, the full format in old Windows versions, like Windows XP, involves overwriting the drive's data with 0 (zeros), but the Full Format on modern versions, such as Windows 10, does not do the same.
If you are interested in recovering data from a formatted drive through CMD or a specialized tool, please read: How to Recover Formatted External Hard Drive Using CMD?
Quick format vs full format - how long will it take
The formatting speed is the factor that most Windows users care about when it comes to quick format vs full format. Here's why the Quick Format is different from the Full Format in terms of speed:
- Quick Format - The primary job of Quick Format is to remove the drive's data and the file system structure, which could be done in a few seconds or minutes.
- Full Format - In addition to the processing of the drive's data and file system structure, a full format could spend hours performing a thorough check and scanning the entire drive for bad sectors that will be marked as unusable.
Quick format vs full format - how to perform
Here's how to select the quick format or full format when you are formatting a drive through File Explorer or Disk Management in Windows:
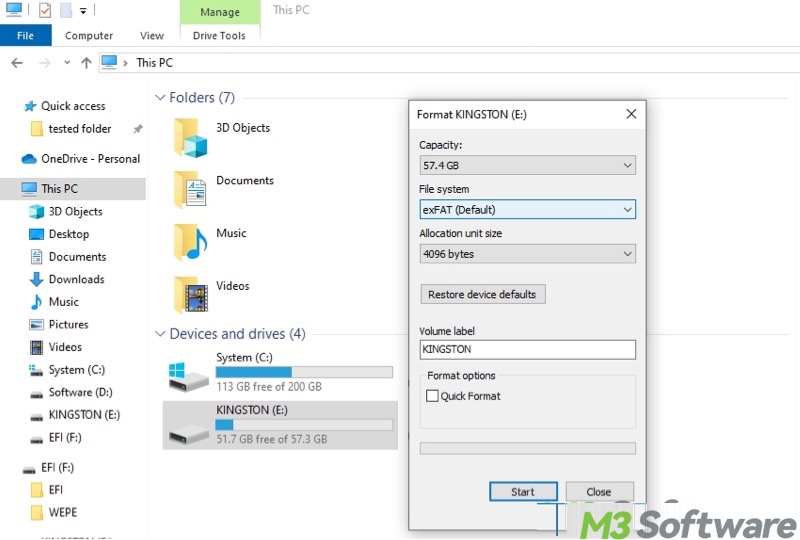
- When formatting a drive through File Explorer, whether to tick "Quick Format" determines how you want to format the drive.
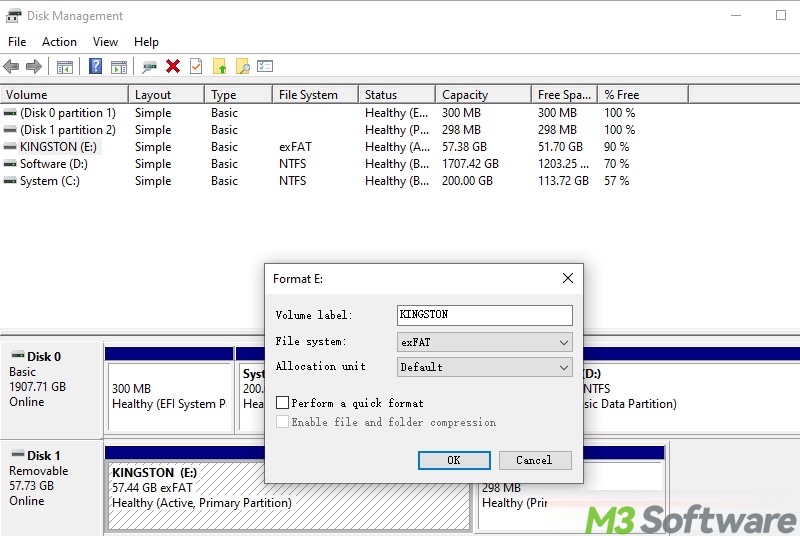
- When formatting a drive through Disk Management, the "Perform a quick format" checkbox decides how the drive is formatted.
Quick format vs full format - which one to choose
Based on the key differences between quick format and full format, quick format is ideal when:
- You want to format a drive quickly (in a few seconds or minutes).
- You are preparing a new drive or reformatting one for other uses.
- You don't need a more secure and thorough data erasure.
- The drive works fine and is in good condition.
A full format is recommended when:
- You're concerned about drive health or want to detect and exclude bad sectors.
- You want to erase the data more thoroughly, making the data recovery more difficult.
- You are going to transfer or sell the drive.
Please share this post if you find it helpful
