Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: This post focuses on Hibernate mode vs. Sleep mode on Windows, primarily elaborating on their functions, the resume speed, and the situations for which they are best suited. -From m3datarecovery.com

When the drop-down menu of the "Power" button on Windows is expanded, the "Hibernate" and "Sleep" options may confuse a lot of Windows users. Both serve the same purpose to a certain degree, but differ in some aspects.
This article is all about Hibernate mode vs Sleep mode on Windows, which guides you through their differences, helping you decide which one to choose.
Hibernate mode vs Sleep mode - Functions
Regarding Hibernation mode vs Sleep mode on Windows, how they work is the biggest difference.
Hibernate mode
When you click the "Hibernate" button, Windows saves your session, including open apps, programs, and files etc., to the hiberfil.sys file stored on HDD/SSD, and then your Windows PC powers off completely.
When you power the Windows PC back on, Windows loads the hiberfil.sys file and restores the exact working state to where you left off, saving you the trouble of reopening apps, programs, or files.
As a side note, the hiberfil.sys can take up much disk space on HDD/SSD. Read the following article for more details: How to Delete Junk Files in Windows 11/10? (8 Methods)
Sleep mode
Windows saves your current session to the RAM and puts your Windows PC into a low-power standby state. This means your Windows PC is not completely powered off, so it can restore your session (e.g., files, apps, programs) in a few seconds.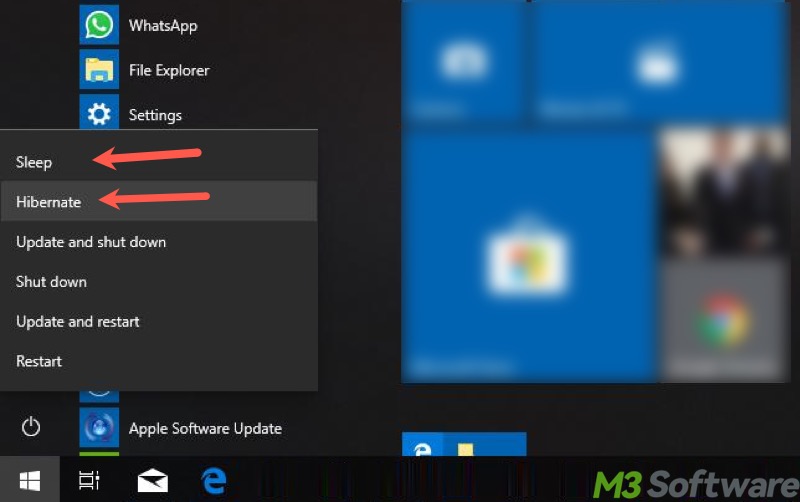
You can share this post with your friends!
Hibernate mode vs Sleep mode - Resume speed
This part discusses how fast Windows can restore the working state under the "Hibernate" and "Sleep" modes.
Hibernate mode
Since your Windows PC is actually completely off and the system has to transfer the sessions from the HDD/SSD into the RAM, resuming can take several seconds to half a minute, which is slower when compared to the sleep mode.
Sleep mode
You can awaken your system instantly from the sleep mode, as Windows keeps everything in RAM, and your Windows PC stays on standby.
Hibernate mode vs Sleep mode - Which one to choose
You can choose hibernate mode or sleep mode based on your needs or the tips below:
Hibernate mode is ideal for
- Long-term breaks, such as overnight.
- The battery is dying
- The laptop charger is temporarily unavailable
Sleep mode is suitable for
- Short-term break
- Users who are coming back soon
- The laptop is plugged in
Hibernate mode vs Sleep mode - How to manage
Follow the steps below to enable/disable the hibernate mode or sleep mode on Windows 10/11
Hibernate mode
The "Hibernate" option is not provided by default on most Windows versions. Therefore, you can manually make it available:
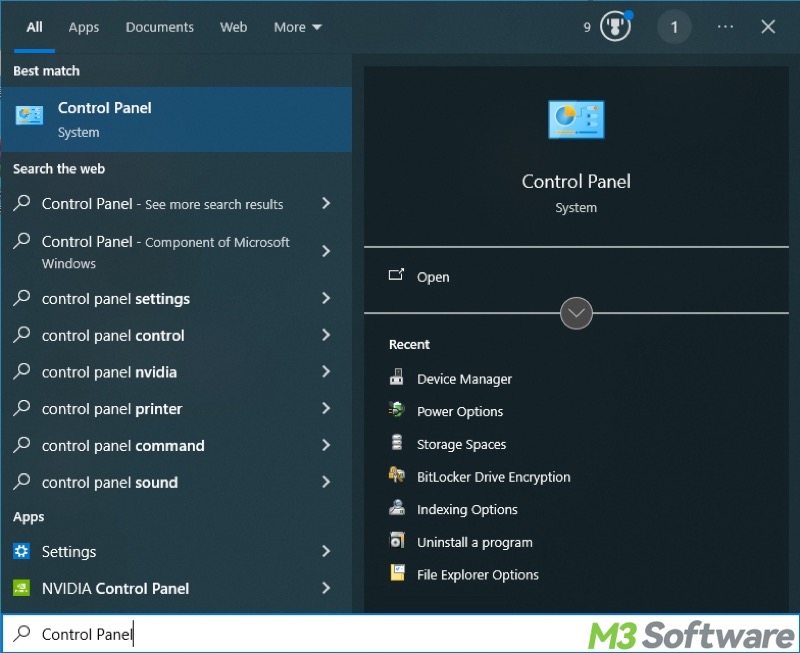
- Open "Control Panel" by searching for it in the Windows search box.
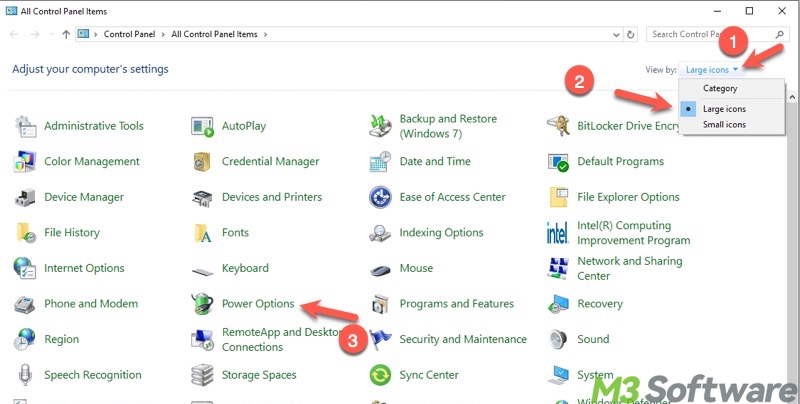
- Switch to "Large icons" and choose "Power Options" from the menu.
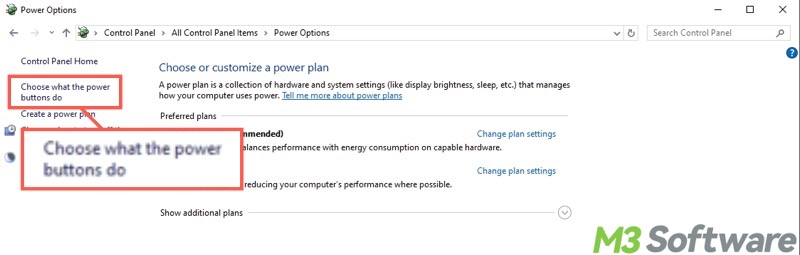
- Tap on "Choose what the power buttons do" from the left side panel.
- Click "Change settings that are currently unavailable."
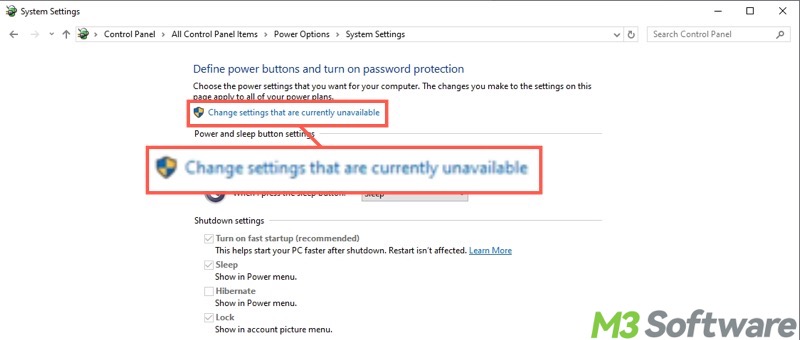
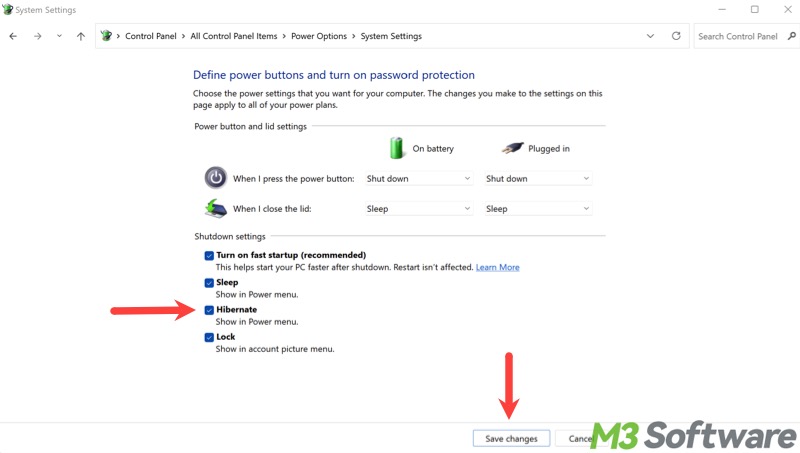
- Tick "Hibernate" and tap on "Save changes."
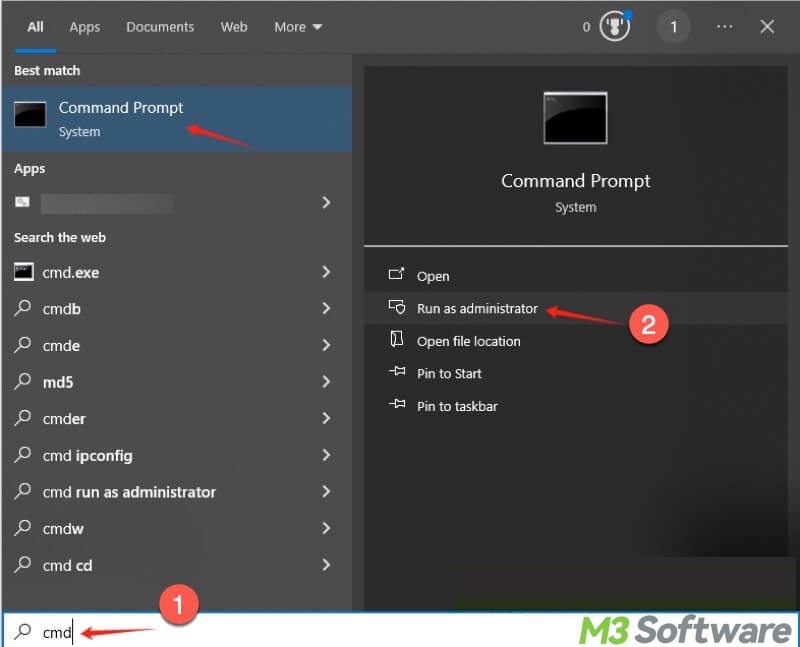
You can also enable the hibernation mode through the Command Prompt:
- Press the "Windows+S" keys to open the Windows search box.
- Type "cmd" and select "Run as administrator."
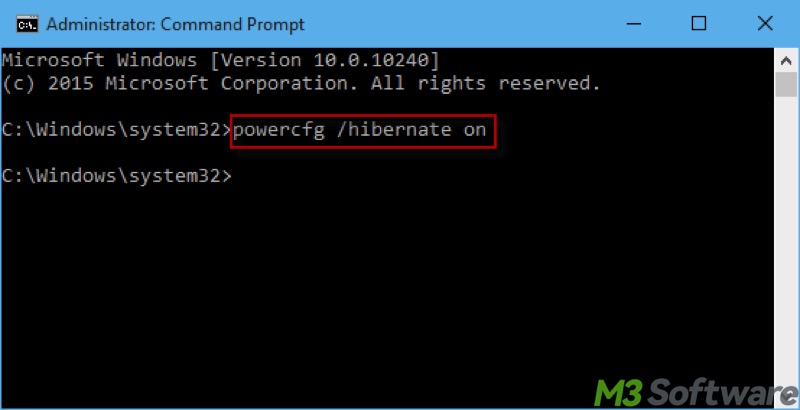
- Input "powercfg /hibernate on" into the command window and hit the "Enter" key on your keyboard.
Sleep mode
Windows may put your Windows PC into sleep mode automatically. In this case, follow the steps below to prevent your Windows PC from entering sleep mode for a certain period of time:
- Press the "Windows+I" keys or click the gear icon in the "Start" menu to open "Settings."
- Choose "System" from the interface.
- Select "Power & sleep" from the left side panel.
- Set the option under the "Screen" and "Sleep" sections to "Never."
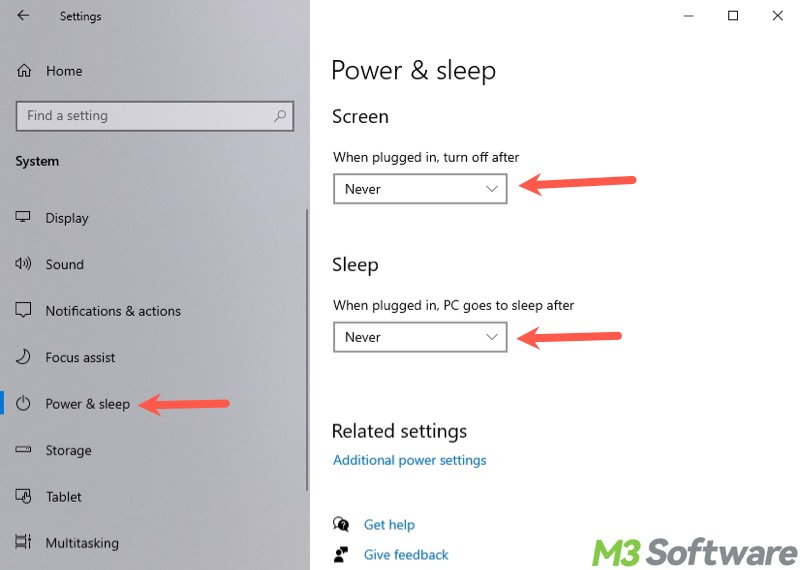
BTW, if your computer screen randomly goes black, changing the “Power & sleep” settings may help.
Comparison table
Here's a quick review of Hibernate vs Sleep mode on Windows 10/11:
| Hibernate Mode | Sleep Mode | |
| Saves the session to | HDD/SSD | RAM |
| Computer power state | computer is completely powered off | computer is in low-power state to maintain RAM |
| Resume speed | several seconds to half a minute | few seconds |
| Ideal for | long-term breaks; when battery is dying or charger isn't available | short-term breaks; when laptop is plugged in |
Conclusion
Both the hibernate mode and sleep mode on Windows can help restore the sessions quickly, so that you don't have to reopen files, apps, programs, and more one by one. By understanding the Hibernate vs Sleep mode, you can be clear about what situations they are best for.
You can share the post by tapping on the buttons below
FAQs about Hibernate mode vs Sleep mode
Hibernate Mode saves your work and settings (alias session) to the hiberfil.sys file on HDD/SSD and then powers down completely. It takes longer to resume but uses no power while off. Sleep Mode saves the session to RAM and keeps your Windows PC in a low-power state, and it typically takes only a few seconds to wake up.
Hibernate is best for longer breaks, like overnight or when traveling with a laptop, since the Windows PC is powered off completely. Sleep is suitable for short breaks, from minutes to a couple of hours.
The Hibernate option is not provided by default. You need to manually make Hibernate available: 1. Open Control Panel. 2. Choose Power Options from the menu. 3. Click Choose what the power buttons do. 4. Click Change settings that are currently unavailable. 5. Tick Hibernate. 6. Click Save changes.
