Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: This post focuses on hot backup vs cold backup, and shows how to choose between hot backup and cold backup to meet different requirements. -From m3datarecovery.com

Performing data backups on a regular basis is highly effective in protecting your data and preventing data loss in this complex digital world. Many backup types are there, and you may be curious about their differences and how to choose among them.
In this article, we will dive into Hot Backup vs Cold Backup and elaborate on the difference between them, including their benefits, limitations, and use cases.
You may also be interested in the incremental backup: Incremental Backup: What Is It & How to Conduct on Windows?
Hot backup vs cold backup - overview of hot backup and cold backup
A hot backup, aka online backup, is performed while the system, database, or application is actively running and in use. It allows you to back up data without shutting down the system or service, which means you can continue accessing and modifying data during the backup process.
The File History feature built into the Windows OS is often regarded as a hot backup method, since it automatically runs in the background and can back up user files while you're using them.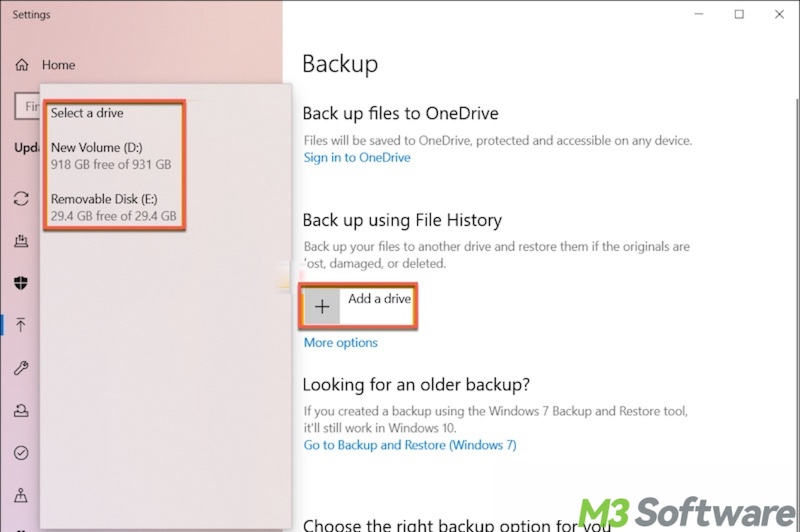
A cold backup, aka offline backup, is applied when the system or application is shut down and not in use. It ensures that no data is being modified during the backup process. The cold backup ensures a consistent copy of the data, and it requires no advanced techniques.
As a side note, if you boot into the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) and run a backup tool to image the disk while the OS is offline, this would be a cold backup. The following post shows how to choose between incremental and differential backup: Incremental vs Differential Backup: Best Guide You Can Find!
You can click the buttons below to share the post
Hot backup vs cold backup - benefits
Here are the benefits when hot backup is used:
- The system or service remains online and operational, ensuring minimal to no downtime and disruption.
- Frequent data changes are allowed.
- Ideal for databases and applications requiring high availability.
The benefits of cold backup are as follows:
- It ensures data consistency, as no data changes can be made during the backup process.
- It is easier to use and manage.
- It is often scheduled during off-hours to avoid a negative impact.
Hot backup vs cold backup - limitations
Here are the limitations of hot backup that most users care about:
- It requires more advanced tools, configuration, and proper tools to guarantee data consistency.
- The hot (online) backup may slightly impact system performance when in use.
- It is not available in all systems and databases.
Limitations of cold backup:
- It is performed offline, so it requires downtime, and it's not suitable for 27/4 operations.
- It requires more manual steps for scheduling and proper configuration.
- Cold backup during high-traffic windows may encounter disruption.
- Improper system shutdown may lead to data corruption or data loss.
Hot backup vs cold backup - which one to choose
Hot backup is recommended when:
- The system or service requires high availability and cannot afford downtime.
- Suitable for 24/7 operations.
- There are frequent data changes throughout the day.
Pick the cold backup when:
- The downtime is acceptable to the system or service.
- Data changes are not frequent.
- Ideal for simpler data backup strategies.
- You don't prefer specialized data backup tools.
Conclusion
Choosing a data backup method that's right for your needs is crucial in maintaining data security and integrity. Regarding hot vs cold backup, the right choice often hinges on whether the downtime is acceptable and how the data backup is scheduled. Of course, combining hot backup and cold backup is feasible and can maximize security.
You can tap on the buttons below to share this post with your friends
