Written by
Yuri ZhangSummary: This article discusses RAM (Random Access Memory), which is different from hard disks. It serves as temporary memory that stores data the computer is currently using, and it is the fastest among others.
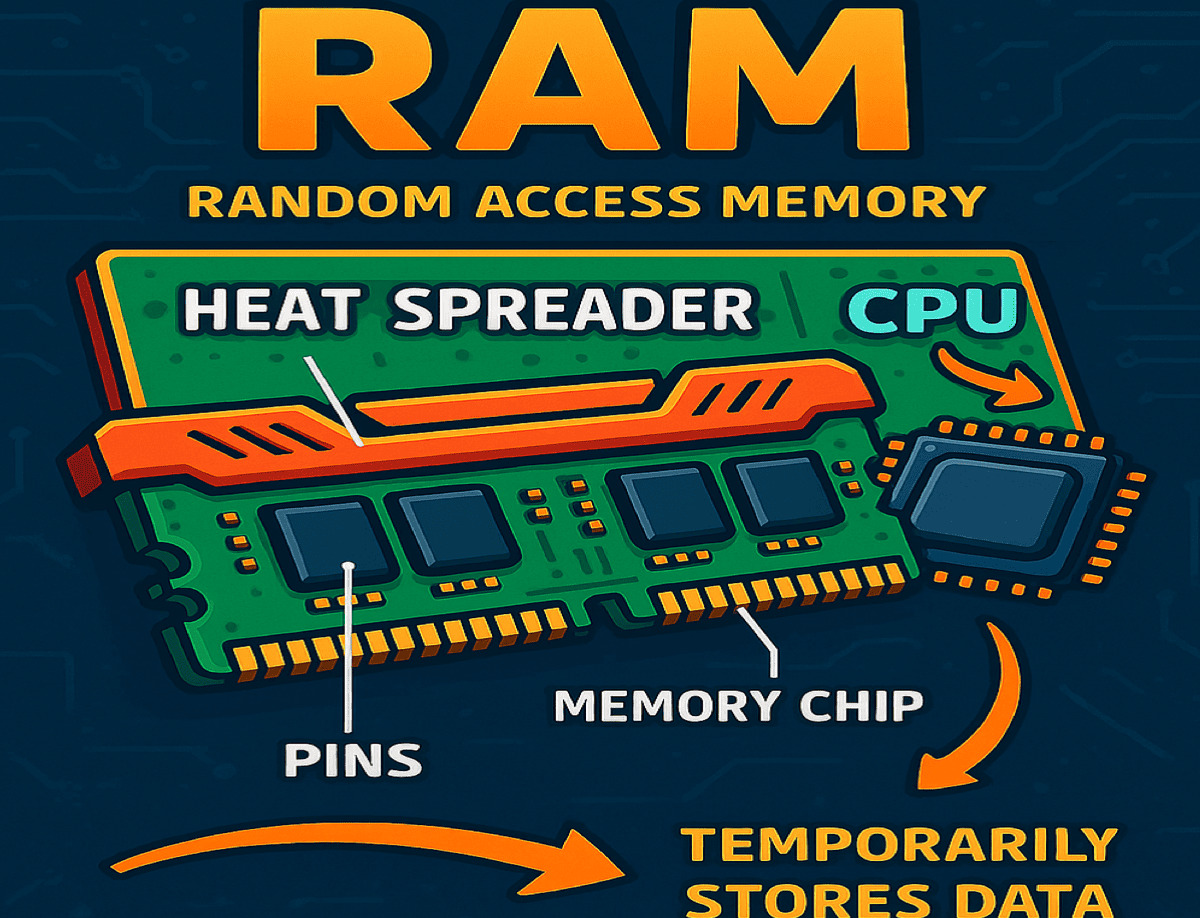
RAM's definition is straightforward, but to help you better understand it, we'll also compare it with other commonly confused storage terms like SSD and hard disk.
If you're new to computers or Windows, you might hear confusing terms like RAM, hard disk, SSD, memory disk, or in-memory storage. These all relate to how our computer stores and accesses data. Let's dive into what they mean and how they affect our computer's speed and storage.
What is RAM?
RAM (Random Access Memory) is our computer's temporary working memory. It stores data and instructions currently in use by the CPU, the brain of our computer.
It is a physical component inside our computer, its stored data is invisible and inaccessible to us because it operates temporarily behind the scenes to support active processes.
RAM is also in-memory, meaning it holds data only while your computer is on. It belongs to volatile memory. When we shut down or restart, all data in RAM disappears.

In contrast, data in hard disk drives (HDDs) stays saved even when our computer is turned off (non-volatile memory). Think of RAM as our computer's desk space. The bigger it is, the more tasks or programs we can work on at once.
Note: HDDs are mechanical devices with spinning disks, so they are slower than RAM. Solid state drives (SSDs) use NAND flash memory (non-volatile), which has no moving parts. So SSDs make our computer start faster and load files quicker than HDDs, but still slower than RAM. Want to learn more? Follow: RAM Drive vs. SSD
Why is a hard disk slower than RAM?
RAM uses semiconductor chips for instant electrical access.
A hard disk drive is a permanent storage device inside your computer. It stores our Windows operating system, programs, files, photos, and videos. A solid state drive (SSD) is a faster type of permanent storage compared to HDDs.
Hard disks use mechanical parts, including spinning disks and moving heads, causing delays known as seek time and rotational latency. These mechanical delays slow down data reading/writing to milliseconds, while RAM works in nanoseconds.
SSDs, although faster than HDDs (no moving parts), still cannot match RAM's speed because of slower flash memory and connection interfaces.
What is “RAM rank”?
This is a more technical detail, but important for understanding RAM speed and compatibility. RAM rank refers to how memory chips are organized on a RAM module. Single-rank means one group of chips accessed at a time; dual-rank means two groups accessed alternately, which can improve performance.
Share this if you intend to know more about this.
What is “memory disk” or “RAM disk”?
A RAM disk (or RAM drive) is a virtual drive created inside your RAM. It looks like a disk drive in Windows Explorer but uses your in-memory RAM. It's super fast because it accesses RAM directly, but all data is lost on shutdown or restart.
We need special software to create a RAM disk (Windows does not provide this natively). Popular RAM disk software includes ImDisk Toolkit, SoftPerfect RAM Disk, and Dataram RAMDisk. However, since it's volatile, all data stored on the RAM disk is lost when the system shuts down unless the software includes features to save and restore the disk image.
How RAM disk works
The RAM disk software reserves a portion of our physical RAM and formats it as a virtual drive with a standard file system like FAT32 or NTFS.
Once created, it appears in File Explorer with its own drive letter (e.g., R:), allowing us to read and write data to it just like a normal disk, except all operations happen in memory, making it exceedingly faster than SSDs or HDDs.
Final thought: How do RAM and storage work together
RAM is a fast, temporary, in-memory workspace (volatile). SSD is fast, permanent flash storage (non-volatile). The hard disk is a slower, permanent mechanical storage (non-volatile).
When we open a program or file, Windows loads data from our SSD or HDD into RAM to speed up access. More RAM lets us open more apps and work smoothly without slowing down. You can either upgrade from HDD to SSD, which boosts speed by making data loading quicker, or use both together to help your computer run efficiently.
Usually, when you start a recovery process, system files stored in the recovery partition in Windows are loaded into RAM to run.
Share and know these basics to help others make smart choices about storage usage on Windows.
