Written by
Wilsey YoungSummary: This article primarily explores what ReadyBoost is on Windows operating systems. Detailed steps about how to enable ReadyBoost on Windows are included. -From m3datarecovery.com

Whenever the RAM on a Windows PC runs out of free space, system performance becomes sluggish, and this can happen frequently, especially on a computer with low RAM (e.g., 1-2 GB).
Upgrading the RAM or replacing an HDD with an SSD is often the first idea that comes to our mind when we are frustrated by unresponsive Windows performance. However, the built-in Windows ReadyBoost feature introduced in this article offers a simpler solution.
What is ReadyBoost? How does it work to improve system performance? How can we enable it? This article covers these questions and additional tips about ReadyBoost on Windows.
By tapping on the following buttons, you can share the post quickly
What is ReadyBoost
Windows ReadyBoost is a built-in feature in Windows that allows users to use an external storage device, typically a USB flash drive or other removable storage device, to extend the memory cache of their Windows computer without adding more physical RAM.
ReadyBoost often comes into play when a computer is under memory pressure or can't support faster memory modules. It can serve as a handy workaround to improve responsiveness.
How does ReadyBoost work
Typically, when a RAM is reaching its limit, Windows swaps the data that's not in immediate use to the Pagefile.sys file on your hard drive. After ReadyBoost is enabled, it functions by transferring data to the free space of a connected removable storage device (e.g., a USB flash drive), which is faster than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
Essentially, ReadyBoost utilizes the connected external storage device to temporarily store files that the system can quickly access, and Windows works in the background to move the files to the ReadyBoost cache and retrieve them when needed. which contributes to relieving the pressure on the system's RAM.
All in all, ReadyBoost can help relieve the pressure on the system's RAM and speed up system performance when running resource-heavy applications or multitasking.
How to enable ReadyBoost on Windows 10/11
First of all, here are some requirements and notes for using ReadyBoost on Windows:
- ReadyBoost operates best on a Windows PC with low RAM (1-2 GB) or a traditional spinning HDD.
- ReadyBoost produces little effect on SSD-based systems.
- The free space on the ReadyBoost storage device won't be available for data storage until the ReadyBoost is disabled.
- The USB flash drive or other removable storage device must be fast enough (Windows will test it for you).
- ReadyBoost is not suitable for heavy workloads, such as video editing, gaming, and more.
After understanding the notes and tips above, here's how to enable ReadyBoost on Windows 10/11:
- Connect a USB flash drive or removable storage device to the Windows PC.
- Double-click "This PC" or "My Computer" on the "Desktop" to open "File Explorer."
- Right-click on the target USB flash drive or removable storage device and choose "Properties."
- Tap on the "ReadyBoost" tab, and the system will check if your storage device is suitable for ReadyBoost.
- Select "Dedicate this device to ReadyBoost" and adjust the space to reserve for caching. You can set it up based on your needs or the recommended value given by the system.
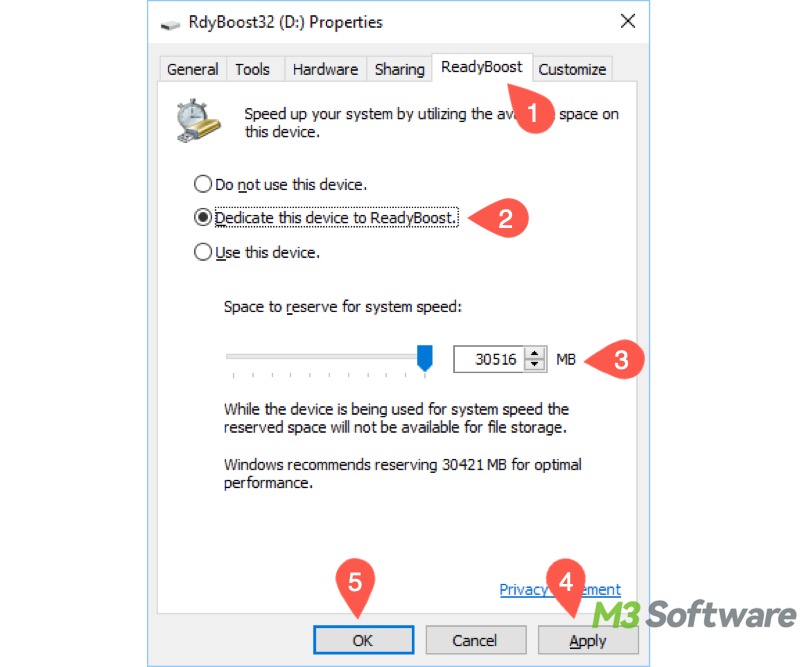
- Click "Apply" and "OK" to save changes.
Conclusion
The built-in ReadyBoost feature on Windows is designed for boosting system performance. The ReadyBoost can save you the trouble of upgrading the physical RAM or hardware, as it uses a USB flash drive or removable storage device as additional virtual memory.
However, ReadyBoost is mostly obsolete on modern devices with large RAM and fast SSDs that provide faster read/write speeds than traditional HDDs. Therefore, ReadyBoost works best on older computers with low RAM size.
Also read:
You can share the post by clicking the buttons below
FAQs about ReadyBoost
ReadyBoost is a Windows feature that allows you to use a USB flash drive or removable storage device as additional cache memory to improve system performance, especially on PCs with low RAM size and slow HDDs.
Typically, ReadyBoost can help when the RAM size is low, the computer runs Windows with a traditional spinning HDD, or users don't want to upgrade RAM physically.
Here are the simple steps of enabling ReadyBoost on Windows: 1. Connect a USB flash drive to your Windows PC. 2. Open File Explorer. 3. Right-click on the inserted USB flash drive and choose Properties. 4. Click the ReadyBoost tab. 5. Select Dedicate this device to ReadyBoost. 6. Click Apply and OK buttons.
